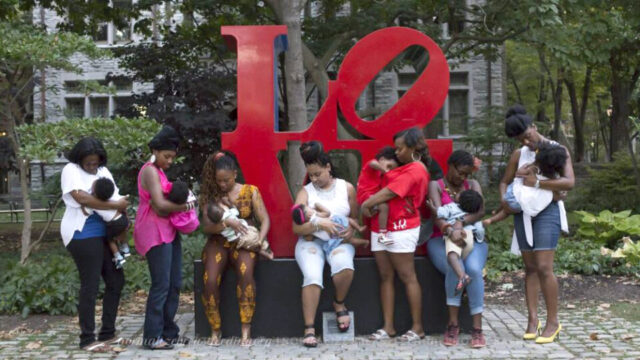Frontline Blog
Social determinants of health
May 2022

The social determinants of health are the conditions and contexts in which people are born, live, learn, work, play, worship, and age that affect a wide range of health, function, quality-of-life, and life expectancy outcomes and risks.
These conditions can be social, economic, or physical, and they include policies, systems, and environments.[i]
Economic stability which includes employers and employment-based systems, as well as public assistance systems, banks, and other systems that impact income and economic well-being.

Education, which includes early childhood education systems, K–12 school systems, colleges, universities, and technical schools, school boards, parent-teacher associations, and other related systems.
Neighborhoods, housing, and the built environment, which includes private and public housing systems, city planning and zoning, developers, road engineering, parks, and other systems that influence physical spaces.

Public health and health care delivery systems, which include public health departments, as well as other organizations that are distinct from, but connected to public health, such as hospital and clinical care systems, mental health agencies, pharmacies, and health insurance systems.

Resources, goods, and services include public transit systems, food systems, and utility providers.

Social and community contexts, which include systems that directly impact social and community structures, including election and voting systems, civic engagement processes, offices of elected officials, and the criminal legal system.
[i] U.S. Department of Health and Human Services, HealthyPeople.gov; Centers for Disease Control and Prevention; Jones, 2014